1. Centralizing wastewater treatment in Assens Municipality
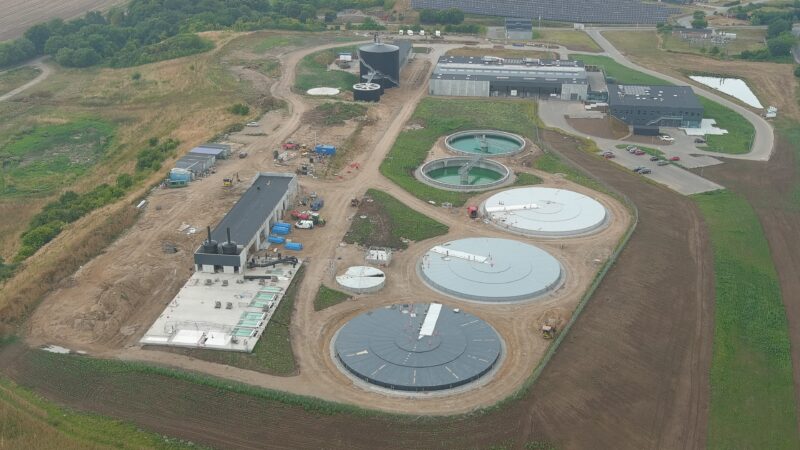

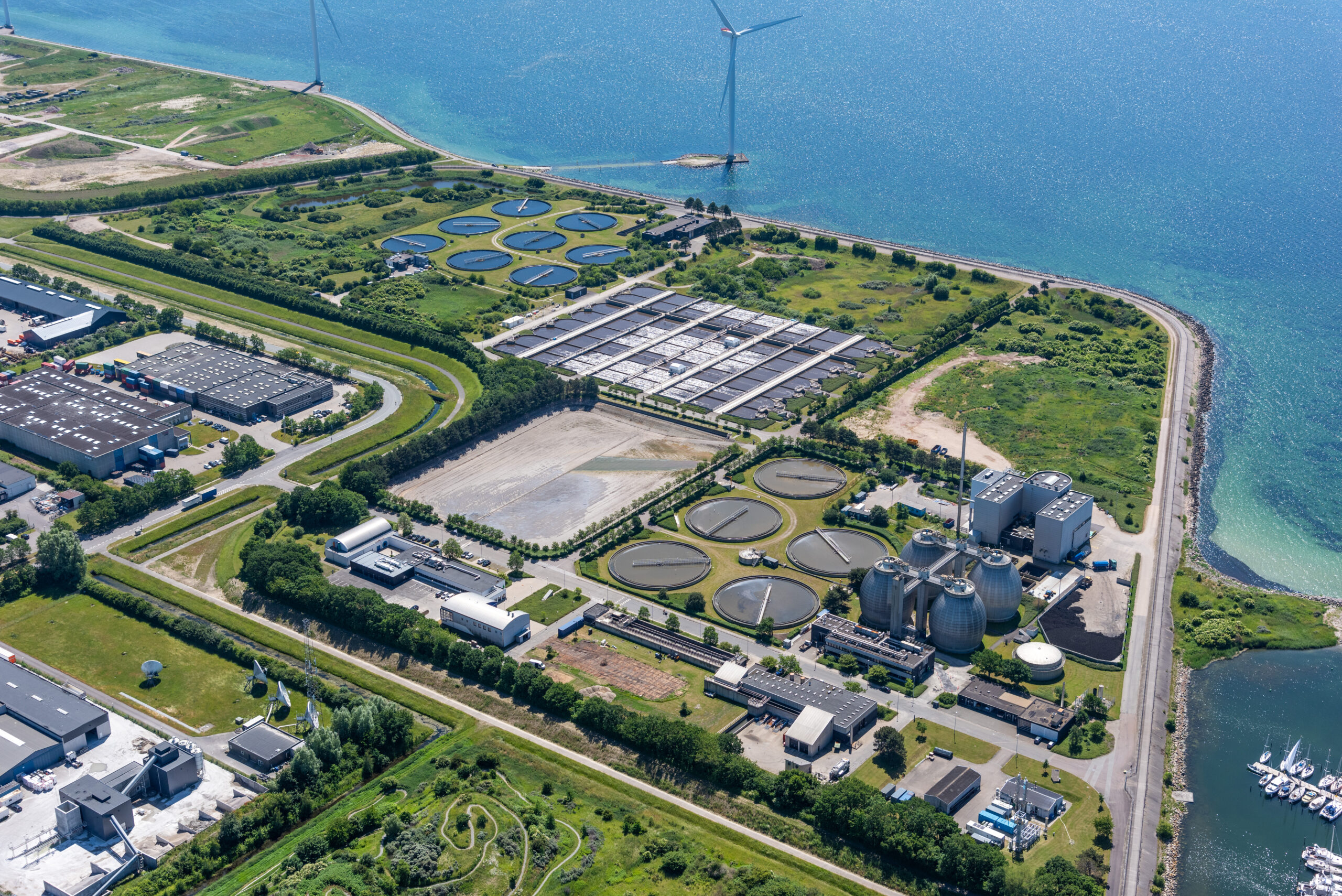
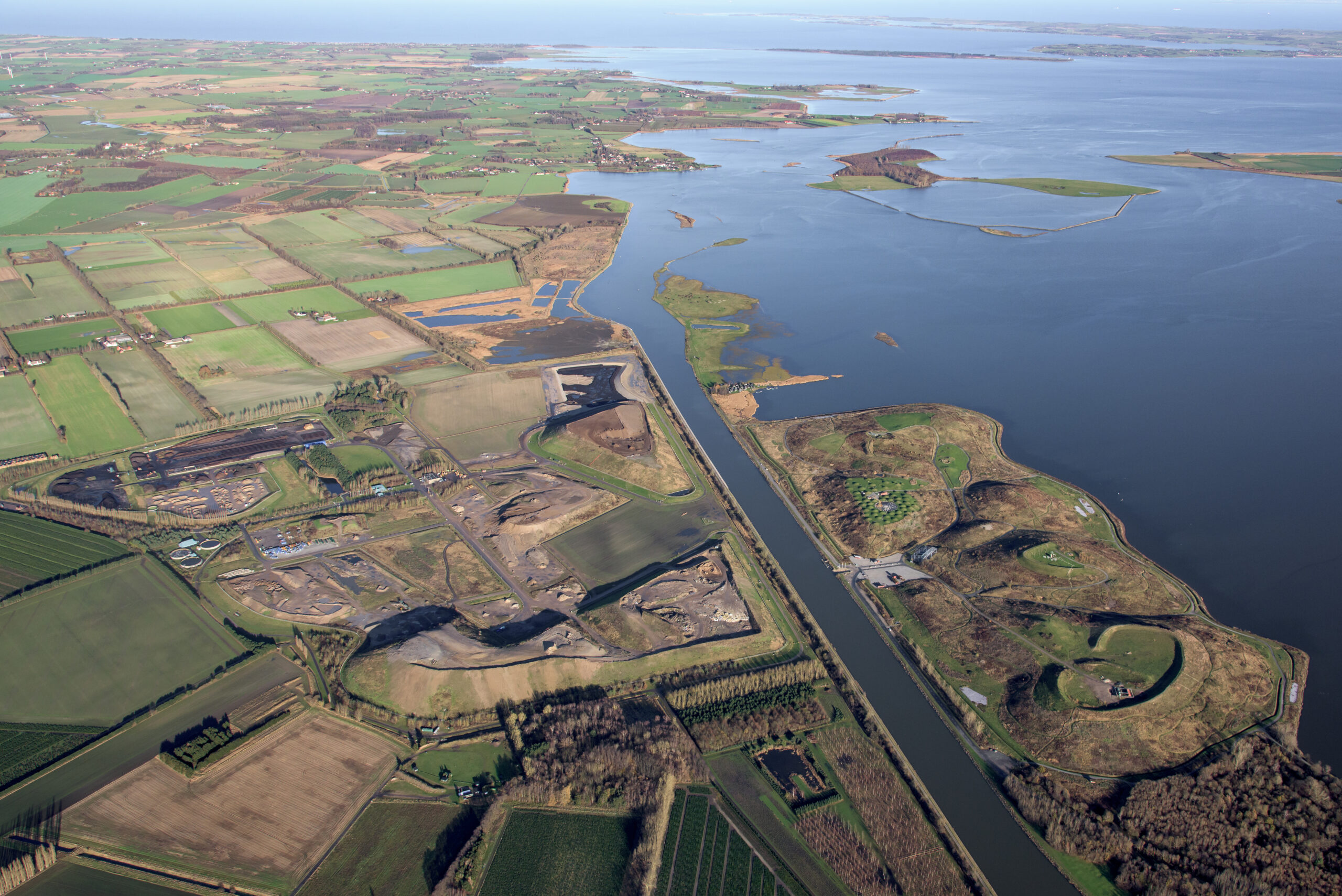
Assens Municipality faced the challenge of outdated and space-constrained wastewater treatment facilities that couldn’t meet future demands. To address this, a new centralized WWTP was established, replacing eight smaller plants, and integrating innovative technology to operate as an energy producer. This facility not only enhances environmental protection and operational efficiency but is also designed to be CO2-neutral by 2029, supporting both urban development and sustainability goals.
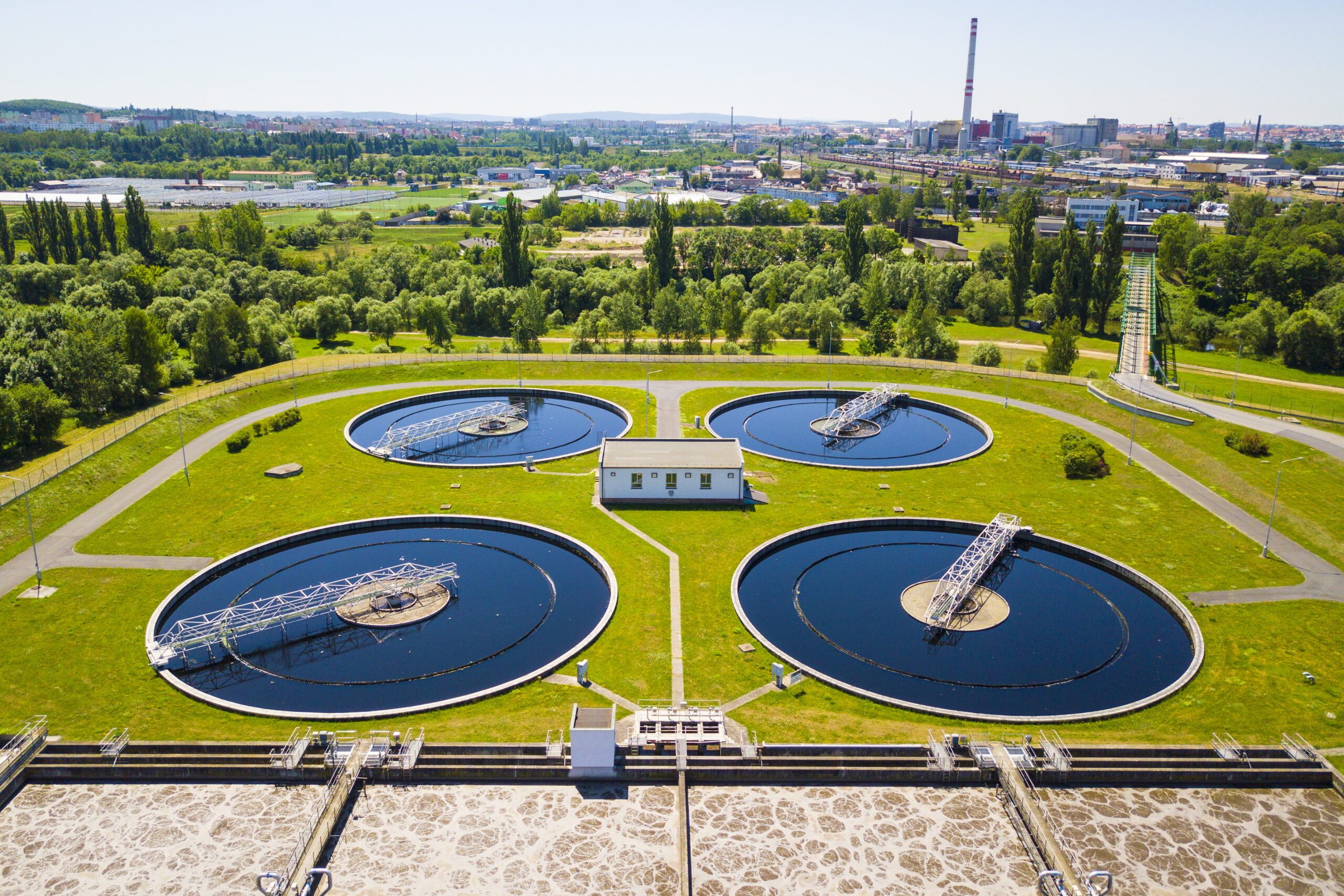
The new wastewater treatment plant, located in a dedicated utility park, consolidates the functions of eight smaller plants, creating a future-ready facility with a capacity of 100,000 person equivalents (P.E.), expandable to 150,000 P.E. The integration of innovative technology enables the plant to operate as an energy producer. Additionally, a biogas plant will be established on-site to maximize energy recovery from industrial wastewater and sludge, further reducing environmental impact.
Solution providers: COWI, Assens Utility, Envidan A/S, NCC A/S, Jacobsen & Bindkilde A/S, & Cubo A/S
Discover the case: From eight to one innovative, centralized wastewater treatment plant